实验八 文件结构
第一题 MS-DOS中磁盘文件的存储结构
实验题目
模拟设计MS-DOS操作系统中磁盘文件的存储结构。
提示
(1)当用户对记录式文件采用顺序存以方式时,用户总是依次地访问一个个逻辑记录,即当访问了第i个记录后,下次总是访问第i+1个记录。所以,当用户采用顺序存取方式访问文件时,只要给出访问要求(读或写)而无需再指出要访问的记录号。
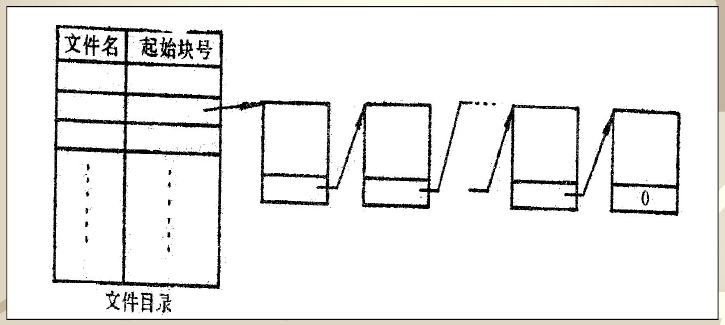
(2)采用链接文件结构,只有读出一个物理块信息后才能从链接字中得知下一个物理块号。所以,当用户要在文件中插入一些信息时,文件系统必须多次地请求启动磁盘读出信息才能做插入工作。
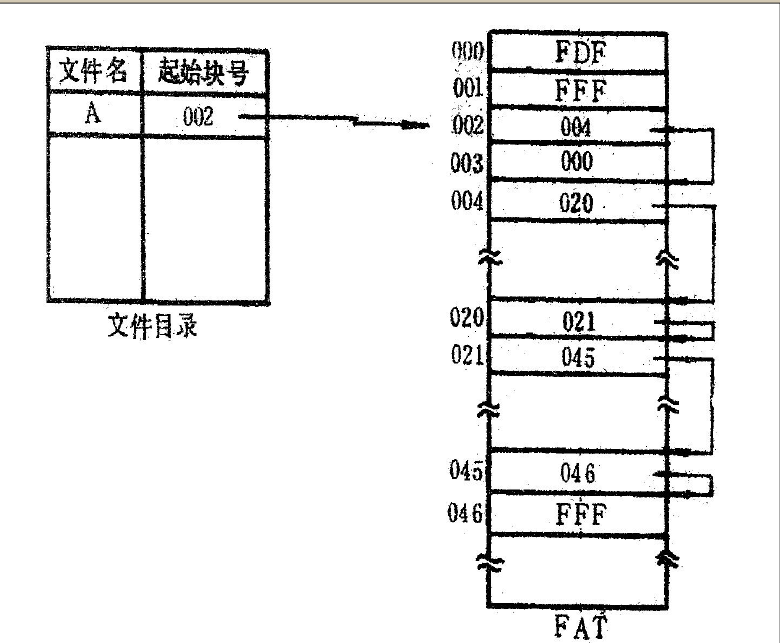
MS-DOS操作系统对链接文件结构作了改进,它是把所有的链接指针集中在一起,存放在文件定位表FAT中。查找链接字时不必读出物理块信息可直接从FAT中得到。
其设计思想是:
(3)假定磁盘存储空间共有32个物理块,模拟设计文件定位表FAT。文件定位表可以用一个一维数组FAT[031]来定义,其中一个元素与一个物理块对应。当FAT[i]=0时,表示第i块为空闲块;当FAT[i]=FFF时,表示链接文件到第i块结束;当在0~FFF时,其值指示链接文件中下一个物理块号。
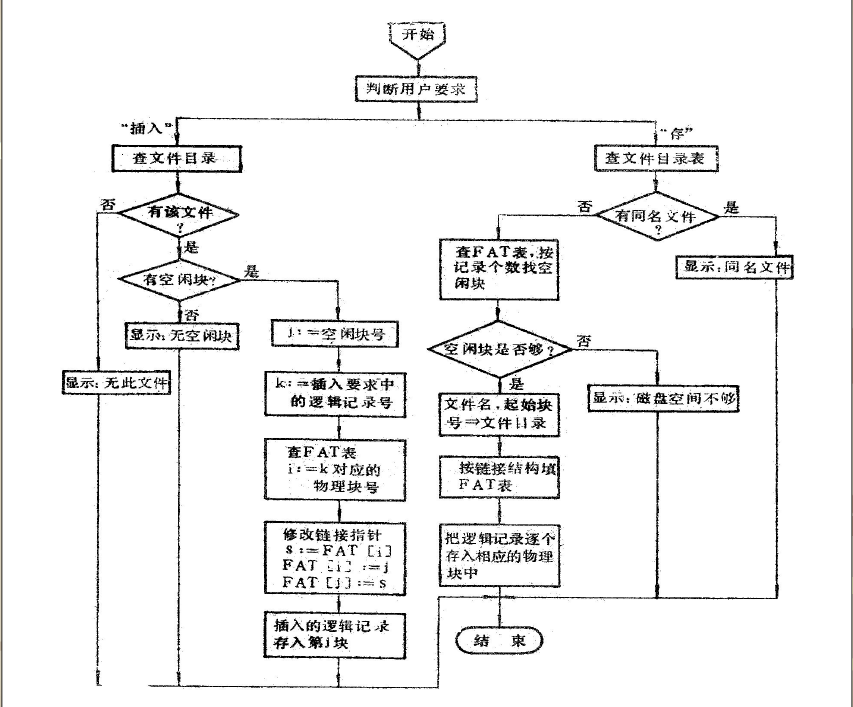
(4)每个物理块只能存放一个逻辑记录,设计一个程序把文件的逻辑结构模拟转换成MS-DOS的链接结构。
程序中使用的数据结构及符号说明
结构体及其数组(数据结构):文件目录信息
struct File //文件目录信息{ string name; int start; int length; 10001 ];
数组(数据结构):文件定位表
整型变量
int cnt = 0 ; int N; int rest;
自定义函数
void init() :初始化void store():存void ins():插入(每次一块)void disCatalog():打印文件目录void disFAT():打印FAT表
源程序并附上注释
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 227 228 229 230 231 #include <iostream> #include <cstring> #include <iomanip> using namespace std;struct File int start; int length; 10001 ]; int cnt = 0 ; int N; int rest; int FAT[10001 ]; void init () "请输入物理块个数:" ;memset (FAT, 0 , sizeof (FAT));void store () "请输入要存入的文件名:" ;for (int i = 0 ; i < cnt; i++)if (catalog[i].name == s)"已存在同名文件!" << endl;return ;int len;"请输入文件记录个数:" ;if (len > rest) "磁盘空间不够!" << endl;return ;int last; for (int i = 0 ; i < len; i++)for (int j = 1 ; j <= N; j++)if (FAT[j] == 0 && j != last) if (i == 0 ) else if (i == len - 1 ) -1 ; break ;"文件保存完毕!" << endl;return ;void ins () "请输入文件名:" ;bool flag = 0 ; int num; for (int i = 0 ; i < cnt; i++)if (catalog[i].name == s)1 ;break ;if (!flag) "无此文件!" << endl;return ;if (rest == 0 )"无空闲块!" << endl;return ;int ins_num; "请输入 插入的逻辑记录在文件中的编号:" ;if (ins_num > catalog[num].length + 1 )"编号过大!" ;return ;int free_block;for (int i = 1 ; i <= N; i++)if (FAT[i] == 0 )break ;int temp_pos = 0 ; int pre; for (int i = catalog[num].start; FAT[i] != -1 ; i = FAT[i])if (temp_pos == ins_num - 1 ) break ;if (ins_num == 1 ) if (ins_num == catalog[num].length) -1 ;"插入完毕" << endl;return ;void disCatalog () "文件目录如下:" << endl;"| 文件名 | 起始块号 |" << endl;for (int i = 0 ; i < cnt; i++)"| " << setw (6 ) << catalog[i].name << " | " << setw (8 ) << catalog[i].start << " |" << endl;void disFAT () "FAT表如下:" << endl;for (int i = 0 ; i <= N; i++)setw (3 ) << i;if (i == 0 )"FDF" << endl;else if (FAT[i] == -1 )"FFF" << endl;else setw (3 ) << FAT[i] << endl;return ;int main () init ();int op = 5 ;while (op)"----------------------" << endl;"1:存" << endl;"2:插入" << endl;"3:查看文件目录" << endl;"4:查看FAT表" << endl;"0:退出" << endl;"请输入操作:" ;"----------------------" << endl;if (op == 1 )store ();if (op == 2 )ins ();if (op == 3 )disCatalog ();if (op == 4 )disFAT ();if (op == 0 )"程序结束!" ;"----------------------" << endl;return 0 ;
运行结果
第二题 模拟便于直接存取的索引文件结构
实验题目
模拟便于直接存取的索引文件结构。
提示
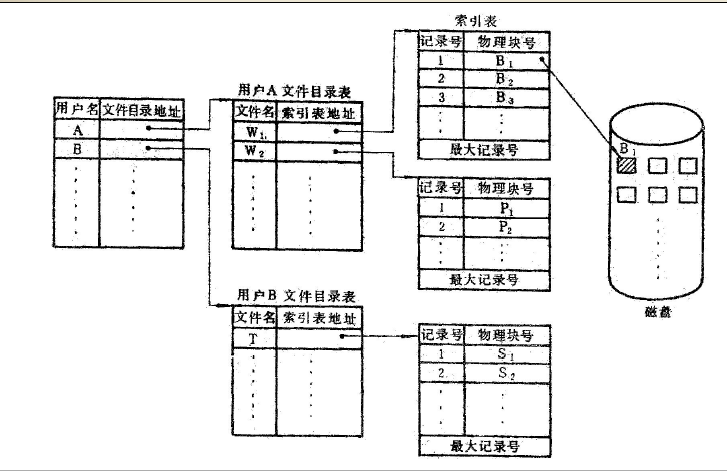
(1)索引文件像链接文件一样,文件的逻辑记录信息可存放在非连续的磁盘存储空间中。但这些存放逻辑记录的存储空间不是按链表的形式链接在一起的,而是采用索引表来指出逻辑记录存放的物理位置。
文件目录与索引表的关系如下图所示:
(2)建立索引文件的过程是:寻找一些空闲物理块;逻辑记录存入这些物理块中;把逻辑记录与物理块的对应关系登记在索引表中。
程序中使用的数据结构及符号说明
整型变量
int rest = 100000 ; int user_cnt = 0 ;
一维数组(数据结构)
bool disk[100001 ]; string user[101 ]; int file_cnt[101 ];
二维数组(数组结构)
int block_cnt[101 ][101 ]; string file[101 ][101 ]; int table[101 ][101 ][101 ];
自定义函数
void init():初始化函数,重置磁盘和用户
int findUser(string username):搜索用户列表,判断用户是否已经存在
int findFile(string username, string file_name):搜索用户的文件列表,判断文件是否已经存在
void addUser():创建新用户
void addFile():添加新文件
void delFile():删除文件
void delUser():删除用户
void disUser():查看用户列表
void disFile():查看用户的文件目录
void disTable():查看某个用户的某个文件的索引表
源程序并附上注释
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 227 228 229 230 231 232 233 234 235 236 237 238 239 240 241 242 243 244 245 246 247 248 249 250 251 252 253 254 255 256 257 258 259 260 261 262 263 264 265 266 267 268 269 270 271 272 273 274 275 276 277 278 279 280 281 282 283 284 285 286 287 288 289 290 291 292 293 294 295 296 297 298 299 300 301 302 303 304 305 306 307 308 309 310 311 312 313 314 315 316 317 318 #include <iostream> #include <iomanip> std ;int rest = 100000 ; int user_cnt = 0 ; bool disk[100001 ]; string user[101 ]; int file_cnt[101 ]; int block_cnt[101 ][101 ]; string file[101 ][101 ]; int table[101 ][101 ][101 ]; void init () for (int i = 0 ; i < 100001 ; i++)0 ;0 ;cout << "磁盘已重置" << endl ;int findUser (string username) for (int i = 1 ; i <= user_cnt; i++)if (user[i] == username)return i;return 0 ;int findFile (string username, string file_name) int usr = findUser(username);for (int i = 1 ; i <= file_cnt[usr]; i++)if (file[usr][i] == file_name)return i;return 0 ;void addUser () string username;cout << "请输入用户名称:" ;cin >> username;if (findUser(username) != 0 )cout << "该用户已存在,创建失败" << endl ;return ;0 ;cout << "用户创建成功" << endl ;return ;void addFile () string username;cout << "请输入要添加文件的用户名称:" ;cin >> username;if (findUser(username) == 0 )cout << "该用户不存在,文件添加失败" << endl ;return ;string file_name;cout << "请输入要添加的文件的名称:" ;cin >> file_name;if (findFile(username, file_name) != 0 )cout << "该用户已经存在同名文件,添加失败" << endl ;return ;int len;cout << "请输入文件的长度:" ;cin >> len;if (len > rest)cout << "磁盘空间不足,存储失败" << endl ;return ;int user_pos = findUser(username);int pos = 0 ;for (int i = 1 ; i <= len; i++)while (disk[pos] != 0 )1 ;cout << "文件存储成功" << endl ;void delFile () string username;cout << "请输入要删除的文件所属的用户:" ;cin >> username;if (findUser(username) == 0 )cout << "没有这个用户,删除失败" << endl ;return ;string file_name;cout << "请输入要删除的文件名称:" ;cin >> file_name;if (findFile(username, file_name) == 0 )cout << "没有这个文件,删除失败" << endl ;return ;int user_pos = findUser(username);int file_pos = findFile(username, file_name);for (int i = 1 ; i <= block_cnt[user_pos][file_pos]; i++)0 ;for (int i = file_pos; i < file_cnt[user_pos]; i++)for (int j = 1 ; j <= block_cnt[user_pos][i + 1 ]; j++)1 ][j]; for (int i = file_pos; i < file_cnt[user_pos]; i++)1 ];for (int i = file_pos; i < file_cnt[user_pos]; i++)1 ];cout << "文件删除成功" << endl ;void delUser () string username;cout << "请输入要删除的用户名称:" ;cin >> username;int user_pos = findUser(username);if (user_pos == 0 )cout << "没有这个用户,删除失败" << endl ;return ;for (int i = 1 ; i <= file_cnt[user_pos]; i++)for (int j = 1 ; j <= block_cnt[user_pos][i]; j++)0 ;for (int i = user_pos; i < user_cnt; i++)for (int j = 1 ; j <= file_cnt[i + 1 ]; j++)for (int k = 1 ; k <= block_cnt[i + 1 ][j]; k++)1 ][j][k];for (int i = user_pos; i < user_cnt; i++)for (int j = 1 ; j <= file_cnt[i + 1 ]; j++)1 ][j];for (int i = user_pos; i < user_cnt; i++)for (int j = 1 ; j <= file_cnt[i + 1 ]; j++)1 ][j];for (int i = user_pos; i < user_cnt; i++)1 ];for (int i = user_pos; i < user_cnt; i++)1 ];cout << "用户删除成功" << endl ;void disUser () cout << "用户列表如下:" << endl ;cout << "| 用户名 | 文件目录地址 |" << endl ;for (int i = 1 ; i <= user_cnt; i++)cout << "| " << setw(6 ) << user[i] << " | " << setw(4 ) << 100 * (i - 1 ) << " |" << endl ;void disFile () string user_name;cout << "请输入要查看文件目录的用户名称:" ;cin >> user_name;int user_pos = findUser(user_name);if (user_pos == 0 )cout << "该用户不存在!" << endl ;return ;cout << "用户" << user_name << "的文件目录如下:" << endl ;cout << "| 文件名 | 索引表地址 |" << endl ;for (int i = 1 ; i <= file_cnt[user_pos]; i++)cout << "| " << setw(6 ) << file[user_pos][i] << " | " << setw(4 ) << 100 * (user_pos - 1 ) +1 ) << " |" << endl ;void disTable () string user_name;cout << "请输入要查看索引表的用户名称:" ;cin >> user_name;int user_pos = findUser(user_name);if (user_pos == 0 )cout << "该用户不存在!" << endl ;return ;string file_name;cout << "请输入要查看索引表的文件名称:" ;cin >> file_name;int file_pos = findFile(user_name, file_name);if (file_pos == 0 )cout << "该文件不存在!" << endl ;return ;cout << "用户" << user_name << "的文件" << file_name << "的索引表如下:" << endl ;cout << "| 记录号 | 物理块号 |" << endl ;for (int i = 1 ; i <= block_cnt[user_pos][file_pos]; i++)cout << "| " << setw(6 ) << i << " | " << setw(4 ) << table[user_pos][file_pos][i] << " |" << endl ;int main () int op = 5 ;while (op)cout << "----------------------------------" << endl ;cout << "1:创建新用户" << endl ;cout << "2:添加新文件" << endl ;cout << "3:删除用户" << endl ;cout << "4:删除文件" << endl ;cout << "5:查看用户列表" << endl ;cout << "6:查看某用户的文件目录" << endl ;cout << "7:查看某文件的索引表" << endl ;cout << "8:查看磁盘剩余空间" << endl ;cout << "0:退出" << endl ;cout << "请输入操作:" ;cin >> op;cout << "----------------------------------" << endl ;if (op == 1 )if (op == 2 )if (op == 3 )if (op == 4 )if (op == 5 )if (op == 6 )if (op == 7 )if (op == 8 )cout << "磁盘剩余空间为:" << rest << endl ;if (op == 0 )cout << "程序结束!" << endl ;cout << "----------------------------------" << endl ;return 0 ;
运行结果
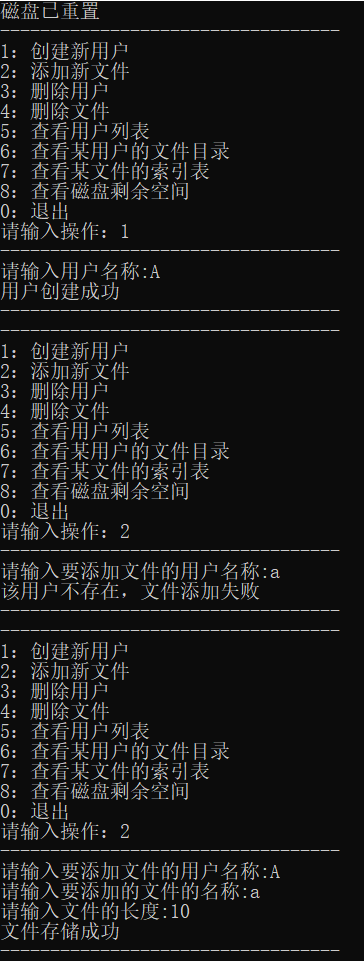
添加用户A及用户A的文件a。
查看磁盘剩余空间
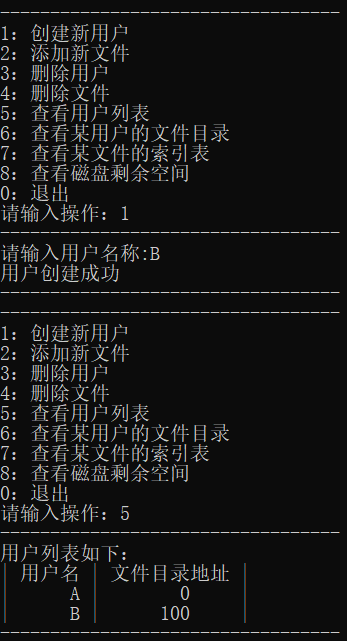
添加用户B,查看用户列表
查看用户A的文件目录和文件a的索引表
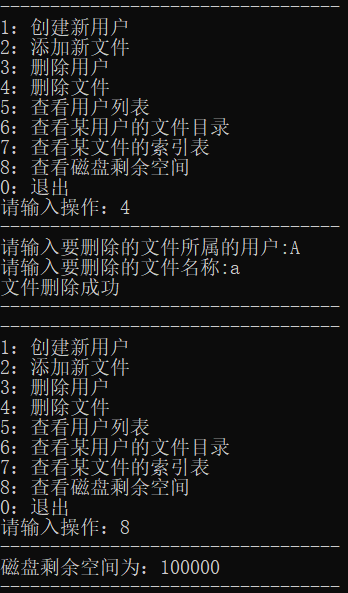
删除文件a,再查看磁盘剩余空间
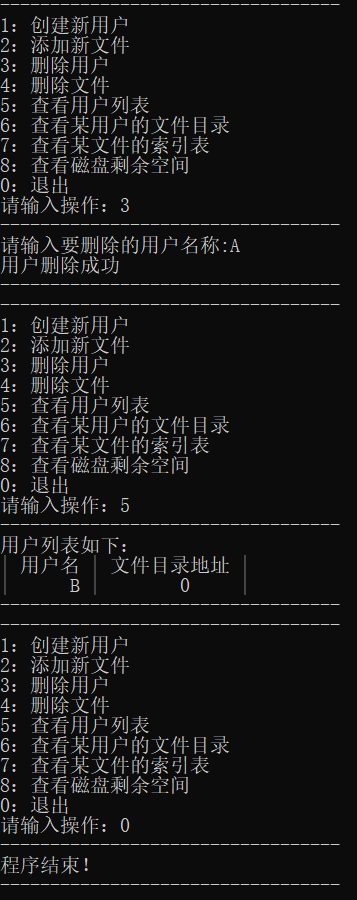
删除用户A,再查看用户列表,最后退出。
思考题
1
链表文件结构和索引文件结构各自的优缺点是什么?
链表文件结构:
优点
① 消除了外部碎片,故而显著地提高了外存空间的利用率;
② 因为是根据文件的当前需要,为它分配必需的盘块,当文件动态增长时,可动态地再为它分配盘块,故而无需事先知道文件的大小;
③ 对文件的增、删、改十分方便。
缺点
① 不能支持高效的直接存取。 要对一个较大的文件进行直接存取, 须首先在 FAT 中顺序地查找许多盘块号。
② FAT 需占用较大的内存空间。
索引文件结构:
优点
① 支持直接访问。当要读文件的第 i 个盘块时,可以方便地直接从索引块中找到第 i 个盘块的盘块号。
② 不会产生外部碎片。
缺点
可能要花费较多的外存空间,系统开销较大。
2
当文件较大时,使得索引表也较大,如果索引表的大小超过了一个物理块,如何进行索引表的存取?
① 采用多级索引方式来解决,使索引表所指的物理块中存储文件信息对应的物理块地址。这样对索引表的长度没有限制,但是空间上的开销比较大。
② 通过分页式内存管理进行存取,使较大的索引表存储时按照块来分割,一定程度上利用了内存空间。但是文件的读取和存储都是分块进行的,而且位置之间没有顺序性,所以存取的算法复杂度较高。
实验心得
该实验使我加深了对两种文件结构的理解。其中在实现MS_DOS磁盘文件的存储结构时,要注意文件定位表实现链接的处理,在插入时把握好头插入、中间插入、尾插入三种情况。实现便于直接存取的索引文件结构时,使用的数组较多,在进行存、删操作的实现时,要把握好这各类数组之间的关系,处理好细节。总之,这次实验使我的动手编程能力有所提升。